Mutation that removes DNA crossword is an intriguing topic that delves into the intricate world of genetics and its impact on biological processes. This exploration unravels the complexities of genetic mutations, their effects on DNA structure, and the captivating realm of crossword puzzle clues that test our knowledge of genetic terminology.
Delving deeper, we uncover the mechanisms by which mutations can disrupt DNA structure and function, leading to genetic disorders with varying inheritance patterns. Understanding these concepts empowers us to appreciate the significance of DNA repair mechanisms in maintaining genetic stability and preventing disease.
Mutation Overview
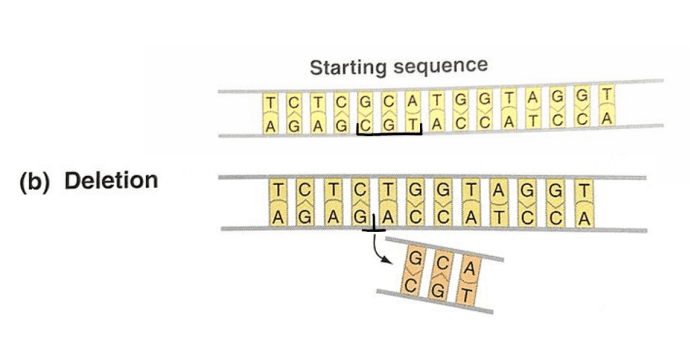
Genetic mutations refer to permanent alterations in the DNA sequence of an organism. They play a crucial role in biological processes, such as evolution, genetic diversity, and adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Mutations can occur in various forms, including:
Types of Mutations
- Point Mutations:Single nucleotide changes, such as substitutions, insertions, or deletions, affecting a single base pair.
- Insertions:Addition of new DNA sequences into the existing genome.
- Deletions:Removal of DNA sequences from the genome.
DNA Structure and Mutations
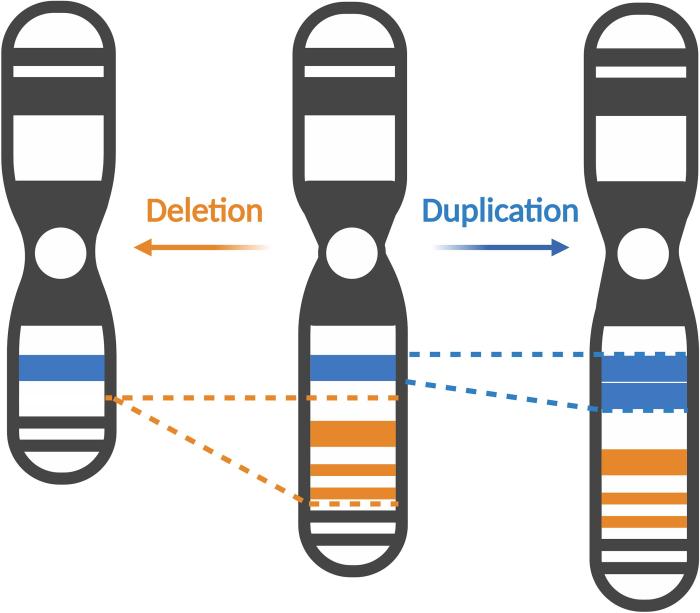
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is made up of two long strands of nucleotides, which are linked together by hydrogen bonds. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base.
There are four different types of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). A always pairs with T, and C always pairs with G. This pairing is known as complementary base pairing.
Mutations are changes to the DNA sequence. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to radiation, chemicals, or errors during DNA replication. Mutations can have a variety of effects on the structure and function of DNA.
Some mutations can disrupt the hydrogen bonding between base pairs, which can lead to changes in the DNA sequence. Other mutations can cause the DNA to break, which can lead to the loss of genetic information.
Disruption of Hydrogen Bonding
One of the most common types of mutations is a point mutation, which is a change in a single nucleotide. Point mutations can disrupt the hydrogen bonding between base pairs, which can lead to changes in the DNA sequence. For example, if an A-T base pair is mutated to a C-G base pair, the hydrogen bonding between the two strands of DNA will be disrupted.
This can lead to a change in the DNA sequence, which can in turn lead to a change in the protein that is produced by the gene.
Other types of mutations can also disrupt the hydrogen bonding between base pairs. For example, insertions and deletions are mutations that add or remove nucleotides from the DNA sequence. If an insertion or deletion occurs in the middle of a gene, it can disrupt the reading frame of the gene.
This can lead to the production of a non-functional protein.
Crossword Puzzle Clues
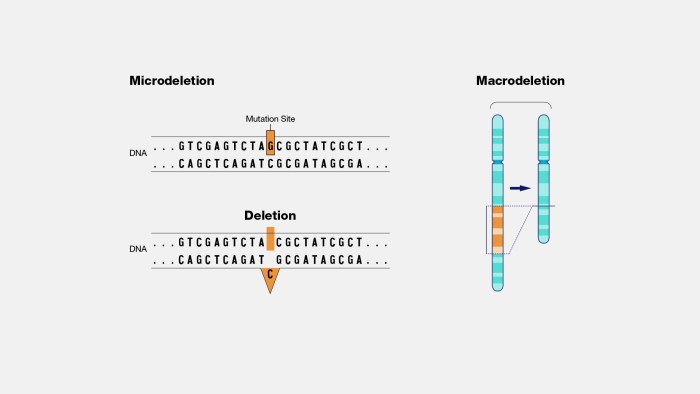
Crossword puzzles often contain clues related to mutations that remove DNA. These clues can be challenging, as they require knowledge of specific types of mutations and the terminology used to describe them.
Specific Types of Mutations
Some crossword puzzle clues may require knowledge of specific types of mutations that remove DNA. For example, a clue like “Mutation that removes a single nucleotide” could refer to a deletion mutation. Other types of mutations that remove DNA include insertions, duplications, and inversions.
Strategies for Solving Crossword Puzzles
There are several strategies that can be used to solve crossword puzzles involving genetics terminology. One strategy is to look for key words that indicate a mutation, such as “remove,” “delete,” or “insert.” Another strategy is to use the context of the clue to infer the type of mutation.
For example, a clue like “Mutation that results in a frameshift” could refer to an insertion or deletion mutation.By using these strategies, crossword puzzle solvers can increase their chances of solving clues related to mutations that remove DNA.
Genetic Disorders
Mutations that remove DNA can result in genetic disorders. These mutations disrupt the normal reading frame of genes, leading to the production of non-functional proteins.
Autosomal Dominant Disorders
- Huntington’s disease:Caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gene, this disorder leads to progressive degeneration of the brain and nervous system.
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
- Cystic fibrosis:Caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, this disorder affects the lungs, pancreas, and other organs due to impaired chloride transport.
- Tay-Sachs disease:Caused by mutations in the HEXA gene, this disorder leads to the accumulation of a fatty substance in the brain, causing progressive neurological damage.
X-linked Disorders
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy:Caused by mutations in the DMD gene, this disorder leads to progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
- Fragile X syndrome:Caused by mutations in the FMR1 gene, this disorder leads to intellectual disability and behavioral problems.
DNA Repair Mechanisms
DNA repair mechanisms are cellular processes that correct mutations and maintain genetic stability. These mechanisms involve identifying and repairing damaged DNA sequences to prevent the accumulation of harmful mutations that could lead to genetic disorders or cancer.
Base Excision Repair (BER), Mutation that removes dna crossword
BER repairs damaged bases by excising the damaged base and replacing it with the correct one. This mechanism is essential for removing oxidative damage caused by free radicals and other environmental factors.
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
NER removes bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by UV radiation or chemical agents. This mechanism involves excising a large segment of DNA containing the damaged site and replacing it with a newly synthesized segment.
Mismatch Repair (MMR)
MMR corrects errors that occur during DNA replication. This mechanism identifies and removes mismatched bases that may have been incorporated during DNA synthesis.
Double-Strand Break Repair (DSBR)
DSBR repairs double-strand breaks, which are the most severe type of DNA damage. This mechanism involves rejoining the broken DNA ends either by homologous recombination or non-homologous end joining.
Defects in DNA Repair Pathways
Defects in DNA repair pathways can lead to genetic disorders characterized by increased susceptibility to cancer and other diseases. Examples of such disorders include:
Xeroderma pigmentosum
A disorder caused by defects in NER, resulting in extreme sensitivity to UV radiation and a high risk of skin cancer.
Ataxia-telangiectasia
A disorder caused by defects in DSBR, characterized by progressive neurodegeneration and increased risk of cancer.
FAQ Corner: Mutation That Removes Dna Crossword
What is a mutation?
A mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of an organism, which can affect the structure and function of proteins and other cellular components.
What is the difference between a point mutation, insertion, and deletion?
A point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide, while an insertion is the addition of one or more nucleotides, and a deletion is the removal of one or more nucleotides.
How do mutations affect DNA structure?
Mutations can disrupt the hydrogen bonding between base pairs, which can lead to changes in the structure and function of DNA.
What are some examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations that remove DNA?
Examples include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease.
How do DNA repair mechanisms help to maintain genetic stability?
DNA repair mechanisms help to correct mutations and maintain the integrity of the genome.