Lab 16-2 Logical Security Concepts delves into the crucial aspects of safeguarding information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This comprehensive guide provides a deep understanding of logical security principles, vulnerabilities, and best practices, empowering readers to implement robust security measures and protect their valuable data and resources.
Logical security, a critical component of cybersecurity, focuses on protecting data and systems within the confines of an organization’s network. By implementing effective logical security measures, organizations can mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and data breaches.
1. Logical Security Concepts
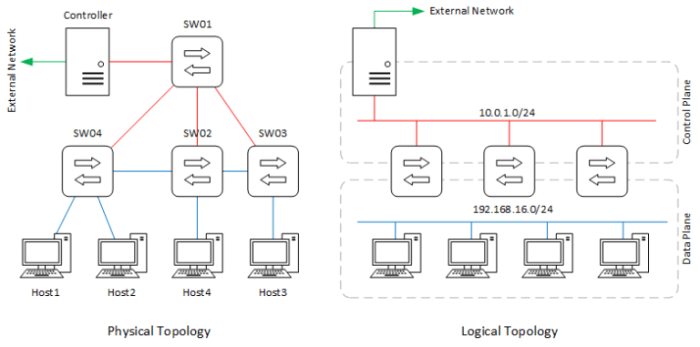
Logical security encompasses the measures and techniques employed to protect digital information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, maintaining system integrity, and ensuring business continuity.
Logical security measures include:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users or devices attempting to access a system or resource.
- Authorization: Granting or denying specific permissions and privileges to authenticated users.
- Access control: Enforcing rules and restrictions to govern who can access what resources and when.
- Encryption: Converting data into an unreadable format to protect its confidentiality.
- Logging and auditing: Monitoring and recording user activities and system events for security analysis and forensic purposes.
2. Vulnerabilities and Threats to Logical Security: Lab 16-2 Logical Security Concepts
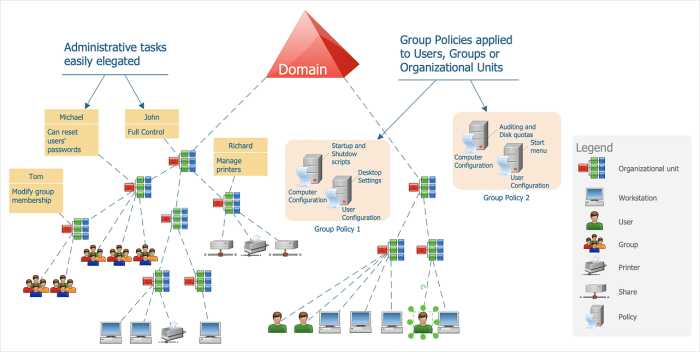
Logical security is vulnerable to a range of threats and vulnerabilities, including:
- Malware: Malicious software that can infect and compromise systems, steal data, or disrupt operations.
- Phishing: Fraudulent emails or websites that trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Brute-force attacks: Attempts to guess passwords or other authentication credentials.
- Buffer overflows: Exploiting software vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to a system.
- Social engineering: Manipulating users into divulging sensitive information or taking actions that compromise security.
These vulnerabilities can have severe consequences, such as:
- Data breaches and theft
- System disruptions and outages
- Financial losses
- Reputation damage
- Legal liabilities
3. Best Practices for Logical Security

To mitigate logical security risks, organizations should implement best practices such as:
- Strong authentication mechanisms (e.g., multi-factor authentication)
- Granular authorization controls
- Secure access control policies
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments
- Security awareness training for users
- Incident response plans and procedures
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. Security awareness training empowers users to recognize and avoid security threats, reducing the risk of human error.
4. Emerging Trends in Logical Security
The evolving technological landscape introduces new challenges and opportunities for logical security. Emerging trends include:
- Cloud security: Protecting data and systems stored in cloud computing environments.
- Mobile security: Safeguarding devices and data in mobile computing environments.
- Internet of Things (IoT) security: Securing connected devices and the data they generate.
These trends present both challenges and opportunities for organizations. By adapting to these changes and implementing appropriate security measures, organizations can enhance their logical security posture and protect their valuable assets.
FAQs
What is logical security?
Logical security refers to the protection of data and systems within the confines of an organization’s network, focusing on access control and authorization mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
What are the common vulnerabilities and threats to logical security?
Common vulnerabilities and threats to logical security include weak passwords, unpatched software, phishing attacks, malware, and insider threats.
What are the best practices for implementing logical security measures?
Best practices for implementing logical security measures include implementing strong authentication mechanisms, enforcing least privilege access control, conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, and fostering a culture of security awareness.
What are the emerging trends in logical security?
Emerging trends in logical security include cloud security, mobile security, and the increasing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning for security monitoring and threat detection.